Injection Molded Microfluidics with HyStem
02/03/20
Publication Title:
Injection Molded Microfluidics for Establishing High-Density Single Cell Arrays in an Open Hydrogel Format
Advanced BioMatrix Products Used:
HyStem® Thiolated Hyaluronic Acid for 3D cell culture within hydrogels
How the products were used:
HyStem® was used to encapsulate cells within a 3D hydrogel for long term cell culture inside an injection molded microfluidic system.
Article Abstract:
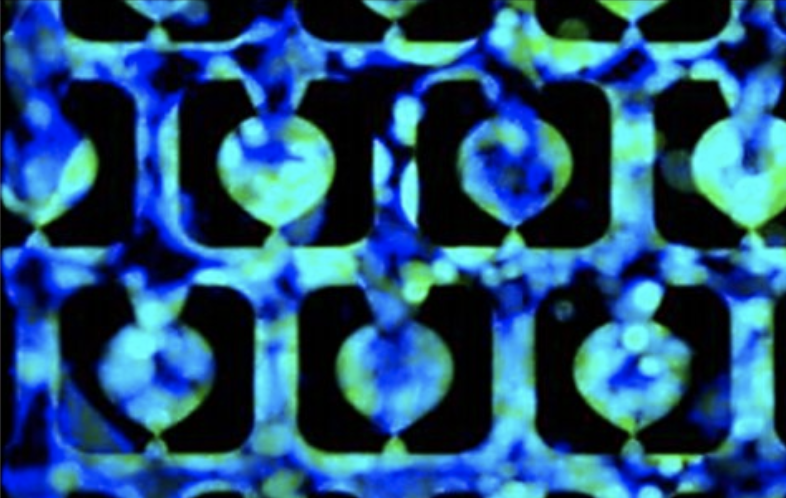
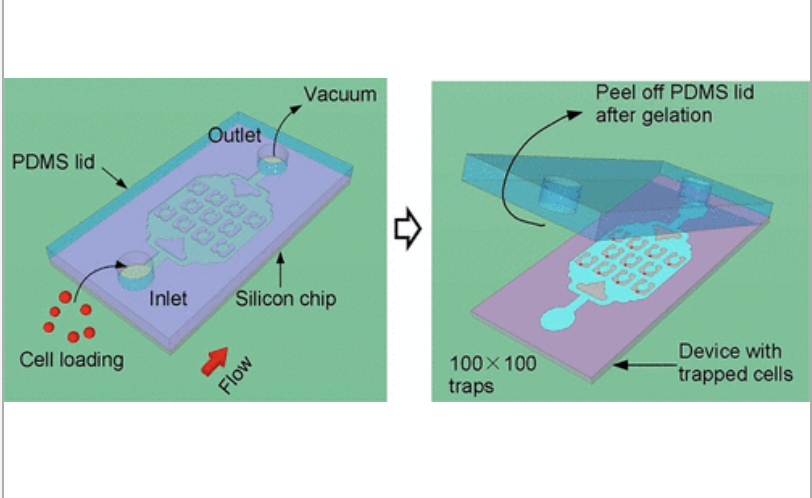
we develop an injection molded microfluidic approach for single cell analysis by making use of (1) rapidly curing injectable hydrogels, (2) a high density microfluidic weir trap array, and (3) reversibly bonded PDMS lids that are strong enough to withstand the injection molding process, but which can be peeled off after the hydrogel sets. This approach allows for single cell patterns to be created with densities exceeding 40 cells per mm2, is amenable to high speed imaging, and creates microfluidic devices that enable efficient nutrient and gas exchange and the delivery of specific biological and chemical reagents to individual cells. We show that it is possible to organize up to 10 000 single cells in a few minutes on the device, and we developed an image analysis program to automatically analyze the single-cell capture efficiency.
The results show single cell trapping rates were better than 80%. We also demonstrate that the genomic DNA of the single cells trapped in the hydrogel can be amplified via localized, multiple displacement amplification in a massively parallel format, which offers a promising strategy for analyzing single cell genomes. Finally, we show the ability to perform selective staining of individual cells with a commercial bioprinter, providing proof of concept of its ability to deliver tailored reagents to specific cells in an array for future downstream analysis. This injection molded microfluidic approach leverages the benefits of both closed and open microfluidics, allows multiday single cell cultures, direct access to the trapped cells for genotypic end point studies.
Link to the publication:
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05099?goto=supporting-info